Yoav Y. Schechner: Research
Generalized Mosaicing
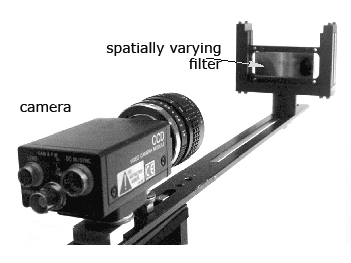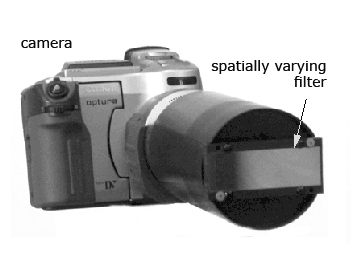
Traditional image mosaicing uses a sequence of images of a scene captured by a moving camera. Generalized mosaicing is a simple and effective method for extracting additional information at each scene point. The key observation is that as a camera moves, it senses each scene point multiple times. We rigidly attach to the camera (either in front or behind the imaging lens) an optical filter with spatially varying properties. When this imaging system moves, each scene point is measured multiple times but under different optical settings. Fusing the data captured in the multiple images yields an image mosaic that includes additional information about the scene. This information can come in the form of extended dynamic range, high spectral quality, polarization, focus/distance sensing or enhancements to other dimensions of imaging.
Publications
- Y. Y. Schechner and S. K. Nayar, “Generalized mosaicing”, Proc. IEEE ICCV - International Conference on Computer Vision, Vol. 1, pp. 17-24 (2001).
- Y. Y. Schechner and S. K. Nayar, “Generalized mosaicing: Wide field of view multispectral imaging,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 24, pp. 1334-1348 (2002).
- Y. Y. Schechner and S. K. Nayar, “Generalized mosaicing: High dynamic range in a wide field of view,” International Journal of Computer Vision 53/3, pp. 245-267 (2003).
- A. Litvinov and Y. Y. Schechner “A radiometric framework for image mosaicing,” Journal of the Optical Society of America - A 22, pp. 839-848 (2005).
- Y. Y. Schechner and S. K. Nayar, “Generalized mosaicing: Polarization panorama,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence 27, pp. 631-636 (2005).
- A. Litvinov and Y. Y. Schechner “Addressing radiometric nonidealities: A unified framework,” Proc. IEEE CVPR - Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vol. II, pp. 52-59 (2005).
- Y. Y. Schechner and S. K. Nayar, “Multidimensional fusion by image mosaics,” in Image Fusion: Algorithms and Applications, pp. 193-221, ed. Tania Stathaki (Academic Press 2008).
Presentations
- “Generalized Mosaics” (13.2 Mb, PowerPoint)
- The above presentation links to four movies: Mosaics (9.4 Mb, AVI), HDR Filter (4.6 Mb, AVI), Variable Spectral Filter (3.9 Mb, AVI) and Spatially Varying Focus (20.8 Mb, AVI).
Related Research
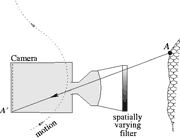 A spatially varying optical filter is rigidly mounted. The camera moves. Each scene point scans through different optical settings.
Mounted filter: Spatially varying neutral density. Scan by camera pan.
A spatially varying optical filter is rigidly mounted. The camera moves. Each scene point scans through different optical settings.
Mounted filter: Spatially varying neutral density. Scan by camera pan.
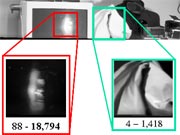 HDR Mosaic from the 8-bit video above.
HDR Mosaic from the 8-bit video above.
 Linear interference filter (LIF).
Mounted filter: LIF. Monochrome camera panning.
Linear interference filter (LIF).
Mounted filter: LIF. Monochrome camera panning.
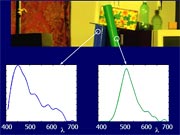 Multispectral Mosaic. Color and Spectral imaging from the monochrome video above.
Mounted filter: Spatially varying polarization and transmissivity. Video camera pan.
Spatially varying focus settings. Effective tilting of image plane. Video camera pan.
Multispectral Mosaic. Color and Spectral imaging from the monochrome video above.
Mounted filter: Spatially varying polarization and transmissivity. Video camera pan.
Spatially varying focus settings. Effective tilting of image plane. Video camera pan.





